Nutrition
· 2 min read
Notes on Amino acids from Nutritional Researcher Christopher Gardner.
 Research Article: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6394758/
Research Article: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6394758/
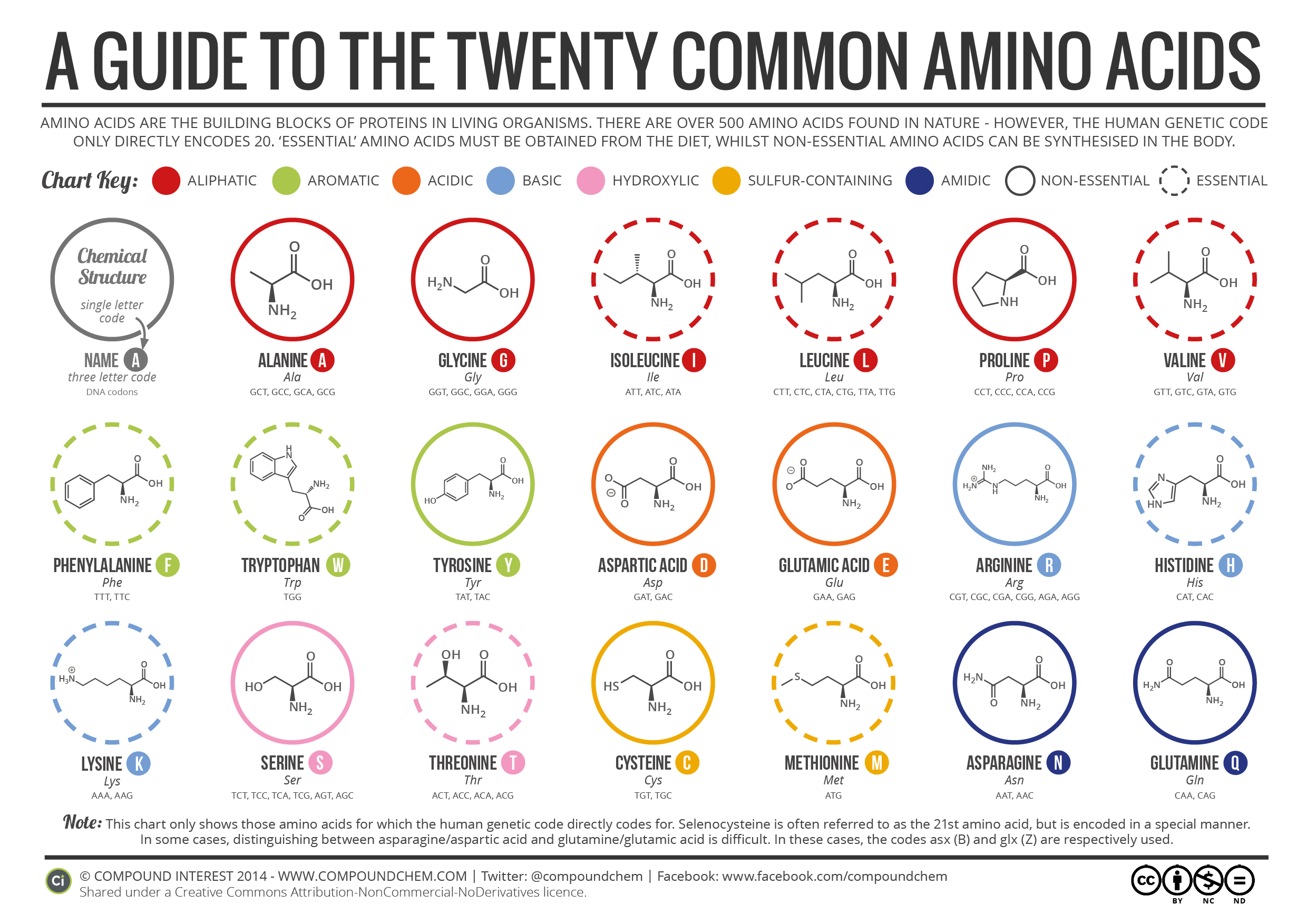
Amino Acids
- Humans need 20.
- 11 are produced by the body: non-essential.
- 9 comes from diet: essential.
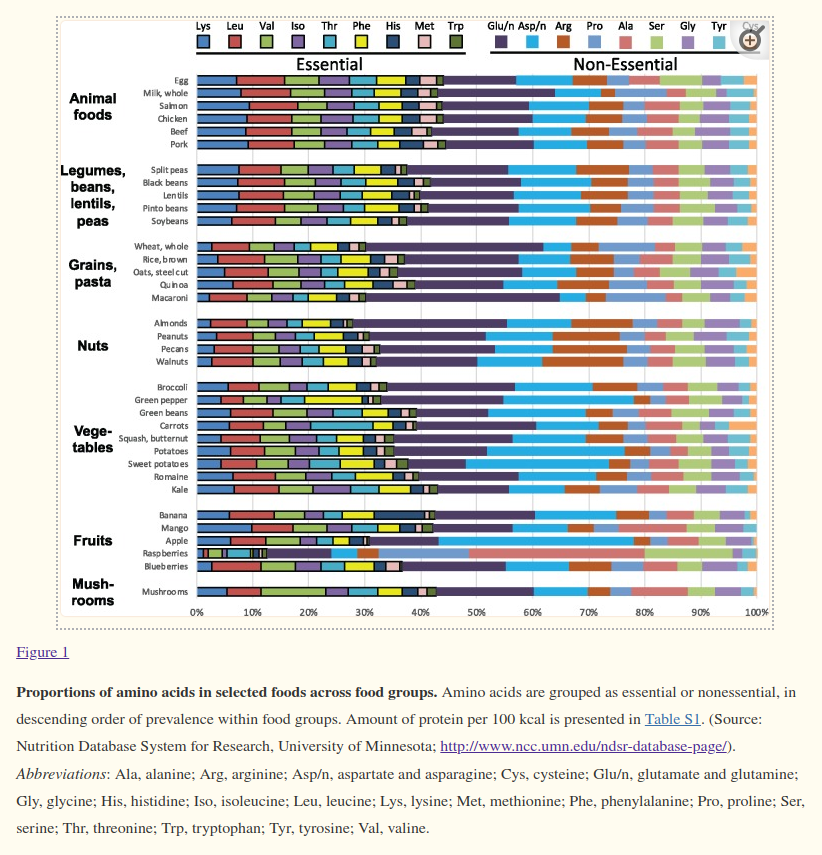
- Plant diet has all amino acids like the animal diet
- Body only absorbs amino acids when they are broken down to their structure, so it does'nt really matter where these come from.
- RDA(Recommened Daily Average) is 0.8 times the body weight and it is already covers 97% of the population, as it already two standard deviations away in the normal distribution.
- 70% of muscle is water and 30% amino acids. If one needs to gain muscle, one calculate how much protein/amino acids are needed.
- 1kg of Gylcogen: Carbohydrate Storage
- Protein can't be stored. At the end of each day, body removes the nitrogen from protein and it will be stored as carbs and fat.
- The nitrogen removed will be turned into Ammonia(NH3) by liver and excreted by Kidney along with some Calcium. People with impaired need to be careful with excess protein.
- Growing kids and pregnant women need to get more protein.
- Plants have all the 20 amino acids and the distribution of amino acids is almost identical with animal protein distribution
- Rice and other grains have low Lysine in comparison to optimal proportion.
- Beans have low methainine and Cystine in comparision to optimal proportion.
- Meat has the optimal distribution of amino acids than plants, but meat has lot of saturated fats, harmones, antibiotics used to grow it, whereas plants have phytochemicals, antioxidants, fibers.